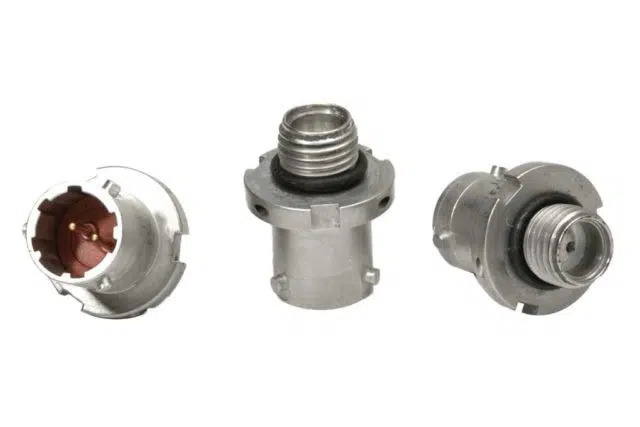
Electric Initiators
Product Description
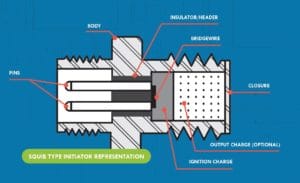
Electric Initiators, also known as Hot Bridge Wires (HBW) are used to provide high reliable critical functions across many industries. An Electric Initiator (EI) converts electrical energy into chemical energy providing a gas or heat output. An electrical input is applied to the EI, heating a small wire, called a bridge wire, which is in contact with the pyrotechnic. The wire quickly heats to the auto-ignition temperature of the pyrotechnic or explosive material. The pyrotechnic material then reacts providing gas pressure and/or flame. The heat and flame can be used to ignite other explosives or propellants while the gas pressure can be used to perform work.
Frequently used names are: initiator, hot bridge wire, igniter, ignitor, detonator, squib, cartridge, or pressure cartridge.
Hot Wire Devices As Safe and Arm Device
A pyrotechnic system consisting of just a power source, and a simple switch or relay powering low voltage device. A hot wire device, squib, or a low voltage hot wire is a non-safe and arm device system. Today, this approach, coupled with a low voltage device, is often implemented for non -safety critical events and not implemented when any of the four critical areas of safety are present.
Hot wire devices are used during payload separation of launch vehicles, the firing of cable cutters, initiating fire suppression cartridges or any other event outside of the four main safety critical events. This type of implementation can be sensitive to environmental stimuli, such as stray voltage, EM, coupling to the pins or cook off fire as well as a variety of other stimuli, which is why they are not used in safety-critical events.
DOWNLOAD DATASHEETS
Initiator 103377-3
Space Standard Initiator 103377-500
Key Features
Electric Initiator Design Guide
How an Electric Initiator Works
An electrical input is applied to the electric initiator, heating a small wire, called a bridge wire, which is in contact with the pyrotechnic. The wire quickly heats to the auto-ignition temperature of the pyrotechnic or explosive material. The pyrotechnic material then reacts providing gas pressure and/or flame. The heat and flame can be used to ignite other explosives or propellants while the gas pressure can be used to perform work.
Configuration Envelope
- Output Thread Size
- Mating Connector
- Overall Length
- Total Mass
- Connector Pin Quantity
- Number of Circuits
- Pin Grounding to Body
- Ground to Cable Shielding
- Cable Definition/Shielding
Environment Capabilities
- Max Temperature
- Max Shock Levels
- Max Vibration Levels
- Acceleration Limit
- Max Storage Temperature
Electric Properties
- Insulation Resistance
- Dielectric Withstanding Voltage
- Circuit Resistance
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Ignition Considerations
- Firing Current (AC-DC)
- Constant Current
- Capacitance Discharge
- Low Voltage Ignition
- High Voltage Ignition
Performance Characteristics
- All-Fire Capability
- No-Fire Capability
- Pressure Output
- Time to Peak Pressure
- Pressure Retention Limits
- Cable/Pin Pull Strength
Common Design Criteria and Test Method Defining Documents
- MIL-DTL-23659 Detail Specification Initiators, Electric, General Design Specification
- AIAA S-113 Criteria for Explosive Systems and Devices on Space and Launch Vehicles
- RCC-319 Flight Termination Systems Commonality Standard
- MIL-HDBK-83578 Criteria for Explosive Systems and Devices on Space Vehicles
- MIL-STD-1901A Munition Rocket and Missile Motor Ignition System Design, Safety Criteria
- MIL-STD-810 Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests
- MIL-STD-1516 Electro-explosive Subsystems, Electrically Initiated Design Requirements and Test Methods
- MIL-STD-331 Fuze and Fuze Components, Environmental and Performance Tests
- MIL-STD-202 Test Methods for Electronic and Electrical Component Parts
- MIL-STD-464 Electromagnetic Environmental Effects, Requirements for Systems
~ Some of the noted documents are cancelled for new designs but are still readily used in the industry. ~
Specifications
- All-Fire, Typical
3.5 amps at 0.999 reliability at 95% Confidence level - No-Fire, Typical
1.0 amps / 1.0 watt, 0.001 probability to fire at 95% lower confidence - Operating Temperature Ranges
As low as -420°F for PacSci EMC’s Space Initiator - Ordnance Output
Deflagration – Tailored peak output pressure performance - Electrostatic Discharge, Typical
25 kVDC from a 500 pF capacitor with a 500 ohm series resistor
Applicable Standards
- MIL-DTL-23659 Initiators, Electric, General Design For; Appendix A: In-Line Initiator Certification
- MIL-STD-1512: Electro-explosive Subsystems, Electrically Initiated, Design Requirements and Test Methods
- DOD-E-83758: Explosive Ordnance for Space Vehicles, General Specification for
- RCC-319: Range Commanders Council Flight Termination Systems Commonality Standard
- MIL-STD-1576: Electro-explosive Subsystem Safety Requirements and Test Methods for Space Systems
Interface
Many features, such as the connector, thread, length, single or dual bridgewire, output, and other features can be customized to meet customer applications.
| PART NUMBER | OUTPUT PRESSURE (PSI) 10 CC Volume | THREAD SIZE | THREAD LENGTH | BRIDGE WIRES | MATING CONNECTOR | PIGTAIL LENGTH (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 103377-3 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-5 | 1300 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-12 | 1600 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-21 | 1450 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 240 | Dual | MS25471-22 | 3.50 |
| 103377-23 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 610 | Dual | MS27467-T9-B98S | |
| 103377-26 | 725 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 400 | Dual | MS27467-E11F-4SA | |
| 103377-29 | 500 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 610 | Dual | MS27467-T9-B98S | |
| 103377-30 | 680 | 7/16-20UNF-3A | 235 | Dual | MS27467-T9-B98S | |
| 103377-32 | 1600 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 250 | Dual | MS3116E8-4S | |
| 103377-34 | 650 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 250 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-43 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-46 | 1450 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 227 | Dual | 2 LEAD WIRES | 10.00 |
| 103377-58 | 580 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 195 | Dual | MS3126E10-6S | |
| 103377-71 | 580 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 213 | Dual | MS24266R8B3S | |
| 103377-99 | 1000 | 3/8-24UNF-2A | 227 | Dual | 2 LEAD WIRES | 63.50 |
| 103377-103 | 1300 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | 2 LEAD WIRES | |
| 103377-105 | 1600 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-106 | 1600 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116E-8-4SW | |
| 103377-107 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-108 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-114 | 1400 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 230 | Dual | MS 3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-115 | 1400 | 3/8-24UNF-3A LH | 230 | Dual | MS 3116P-8-4SW | |
| 103377-119 | 390 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-122 | 1600 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-129 | 1600 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 250 | Single | MS3899/26WA 98SN | |
| 103377-130 | 720 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | 4 LEAD WIRES | 6.15 |
| 103377-137 | 1000 | 9/16-18UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS27467T11F04S | |
| 103377-140 | 500 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-148 | 1400 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | 4 LEAD WIRES | 21.50 |
| 103377-160 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-161 | 500 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116E8-4S | |
| 103377-166 | 1250 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 393 | Dual | MS27467E11F4SA | |
| 103377-179 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-186 | 1300 | 7/16-20UNF-2A | 300 | Single | 2 LEAD WIRES | 2.50 |
| 103377-187 | 2500 | 7/16-20UNF-2A | 300 | Single | 2 LEAD WIRES | 2.75 |
| 103377-191 | 650 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 217 | Single | MS3116P8-2S | |
| 103377-206 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Single | 4 LEAD WIRES | 3.47 |
| 103377-210 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 223 | Single | 2 PIN | |
| 103377-212 | 1450 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 343 | Dual | MS27467-11F-4SA | |
| 103377-219 | 2500 | 1/2-20UNF-2A | 383 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-241 | 1780 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 153 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-258 | 350 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 330 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-291 | 2050 | 1/2-20UNF-2A | 250 | Dual | PC06-8-4S | |
| 103377-300 | 650 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 330 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-324 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Single | MS38999/26WA98SN | |
| 103377-334 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Single | MS3116P8-2S | |
| 103377-335 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A LH | 257 | Single | MS3136P8-2SW | |
| 103377-336 | 925 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 290 | Single | MS3116P8-2SX | |
| 103377-343 | 390 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 215 | Single | MS3112E-14-5P | 12.00 |
| 103377-347 | 1400 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Single | 2 LEADWIRES | 49.00 |
| 103377-351 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | MS27467T11F04S | |
| 103377-359 | 1600 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 143 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-362 | 450 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Single | 2 LEAD WIRES | 10.00 |
| 103377-371 | 1000 | 7/16-20UNJF-3A | 220 | Single | D38999/26MA98PN | 31.23 |
| 103377-407 | 10500 | 3/4-16UNF-2A | 616 | Dual | MS3116E-8-4S | |
| 103377-415 | 300 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A LH | 237 | Single | ST396G8N2SX2 | |
| 103377-416 | 300 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A LH | 203 | Single | MS3116P8-2S | |
| 103377-421 | 650 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A | 205 | Single | MIL-C-38999 | |
| 103377-423 | 1600 | 3/8-24-UNF-3A | 257 | Dual | MS3116-8-4S | |
| 103377-424 | 650 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A | 215 | Single | 2 Wire Pigtail | 20.50 |
| 103377-426 | 1600 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 250 | Single | MS38999/26FA98SN | |
| 103377-429 | 650 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A | 183 | Single | MS3116P8-2S | |
| 103377-430 | 650 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 168 | Dual | MS3126E106S | |
| 103377-432 | 925 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-435 | 600 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 213 | Dual | MS24266R8B3S | |
| 103377-437 | 1300 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 233 | Dual | MS3116P-8-4S | |
| 103377-443 | 2300 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 380 | Dual | MS3116E-8-4S | |
| 103377-444 | 988 | 7/16-20UNF-3A | 220 | Single | D38999/20WA98SN | 15.22 |
| 103377-447 | 5100 | 1/2-20UNF-3A | 288 | Single | D38999/26KA98SN | |
| 103377-449 | 650 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A | 310 | Single | MS3116P8-2S | |
| 103377-450 | 663 | 3/8-24UNF-3A | 335 | Dual | MS3116E8-4S | |
| 103377-500 | 650 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A | 310 | Single | MS3116P8-2S | |
| 103377-501 | 150 | 3/8-24UNJF-3A | 310 | Single | MS3116P8-2S |
FAQ's
-
What does bridge wire mean?
A small wire that transfers energy.
-
Do you have off the shelf availability?
Our -3, -32 and -500 parts are generally available to ship within 2 months.